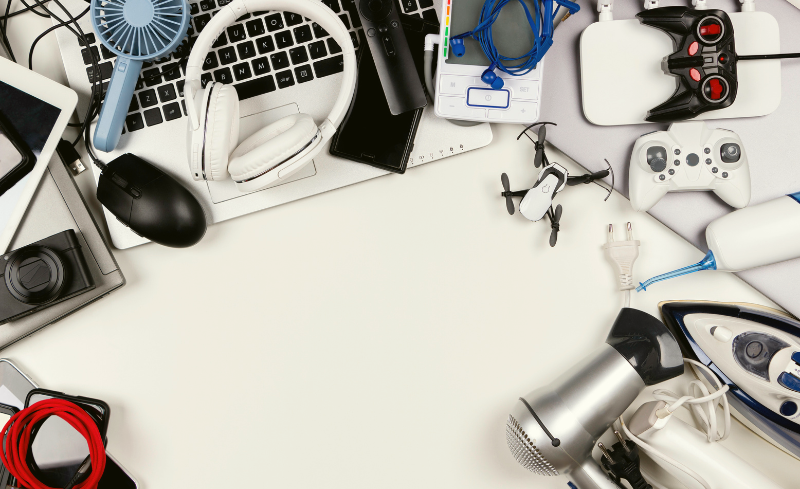
Every 14th of October is International E-waste Day, a key reminder of the environmental challenges and opportunities presented by the management of Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE). This waste represents a threat due to its toxic components but is also an opportunity to recover valuable materials, boost the Circular Economy and reduce the environmental impact. In this article we explain how efficient management of WEEE benefits both the environment and businesses, and how we can all implement sustainable practices to reduce its impact.
ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC WASTE MANAGEMENT (WEEE)

International Electronic Waste Day is on October 14th and at TMA we want to contribute our experience in comprehensive waste management and share our commitment to the efficient management of WEEE to contribute to generating a positive impact on the environment and the Circular Economy.
We must be aware of the growing generation of Electrical and Electronic Waste (WEEE) and how we dispose of and/or recycle it when the useful life of the technological elements we use ends.
“Technology moves the world, but recycling makes it sustainable” — Bill Gates.
Digitalization allows us to advance and improve in many aspects of our daily lives, both personal and professional, but this progress should not be at the expense of sustainability and care for the environment.
We use and dispose of a large amount of electrical and electronic waste, from household appliances to mobile phones, computers, e-books, batteries…, and WEEE contains valuable materials that, if managed properly, can be recycled and recovered, but can also release hazardous substances if not treated responsibly.
Have you ever stopped to think about how many electronic and electrical devices we use every day? Look around you: from phones, tablets, e-books, smart TVs… to electric toothbrushes, microwaves, fans, razors, etc…
Without these devices, modern life would be difficult to imagine. Recycling and giving a “second life” to these products is easier than it seems. If we get involved in recycling them, we will be able to avoid negative consequences for the environment.
Many of these electrical and electronic devices contain highly polluting components and, at the end of their useful life, they can quickly become hazardous waste. It is crucial that we all enjoy the benefits of technology during its useful life and that we are very aware of how to act to recycle and dispose of WEEE correctly.
THE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT OF WEEE (E-WASTE)
WEEE (or e-waste) is the material from electrical and electronic devices that have reached the end of their useful life. This includes the device itself and also all its components, subassemblies and consumables that are in the product at the time of disposal.
Here is a more detailed list of waste that is considered WEEE:
-
- Large household appliances: refrigerators, washing machines, dryers, dishwashers, and other large appliances used in the home.
- Small household appliances: vacuum cleaners, irons, toasters, mixers, hair dryers, among others.
- Computer and telecommunications equipment: computers, laptops, printers, mobile phones, routers and other technological devices.
- Consumer electronics: televisions, cameras, audio equipment, DVD players, video game consoles, etc.
- Power and electronic tools: drills, power saws, gardening equipment, and similar tools that run on electricity.
- Toys and sports equipment: toys that contain electronic components, such as remote-controlled cars, handheld video game consoles, or electronic sports equipment.
- Medical devices: electronic equipment used in the medical field, such as heart rate monitors, digital thermometers, etc.
- Monitoring and control instruments: thermostats, smoke detectors, industrial thermometers, and other devices that have monitoring or control functions.
- Photovoltaic panels: solar panels are also classified as WEEE when they reach the end of their useful life.

It is estimated that more than 50 million tons of WEEE are generated worldwide each year, a figure that continues to increase.
The components of WEEE include valuable materials such as precious metals (gold, silver, copper), but also hazardous substances. For this reason, the efficient and responsible management of this waste is key to avoiding damage to the environment and human health.
Many WEEE contain hazardous substances such as cadmium, mercury, lead, arsenic, phosphorus, toxic oils and gases, which damage the ozone layer and contribute to global warming, and can also filter into the soil and contaminate water.
If WEEE is managed properly, we can avoid environmental damage and we can take advantage of the valuable materials it contains, such as precious metals, plastics and other recyclable components.
If WEEE is not managed correctly, the negative environmental impact does not compensate for the technological utility it has had.
«Technology should improve our lives, not worsen our planet.» – Tim Cook
For this reason, comprehensive, efficient and sustainable management of WEEE must be a priority.
HOW COMPANIES CAN MANAGE WEEE EFFICIENTLY

Companies play a key role in the sustainable management of WEEE, both because of their environmental responsibility and because of the economic and reputational benefits that good management can bring them. Below, we explore various ways and positive benefits for companies that manage their WEEE efficiently and responsibly.
Reuse and repair programs
There are many opportunities for reusing or repairing devices. By extending the life of electrical and electronic equipment, the amount of waste generated is reduced and contributes to greater sustainability. Buyback programs or donations of electronic devices in good condition can be carried out, so that they can be reused by other users.
Selective collection
One of the measures that companies can implement is a selective collection system for their WEEE. This involves having specific containers for the collection of unused electronic devices, which will then be sent to specialized recycling facilities. It is important to have a waste management provider that provides the appropriate containers and packaging to transport WEEE.
Regulatory compliance and avoiding penalties
Complying with regulations helps companies avoid penalties and fines and improves their reputation as environmentally responsible companies.
Recovery of valuable materials
For companies that manage large volumes of electronic waste, such as technology manufacturers, recycling these materials is a significant economic opportunity: they can reduce their production costs and minimize their ecological footprint.
Improving corporate reputation (CSR)
Companies that adopt responsible management of their WEEE demonstrate their commitment to sustainability and the environment. This improves their image and reputation with consumers: people are aware and willing to support companies that have a clear approach to sustainability and responsible waste management.
Contribution to the Circular Economy
It is essential for companies that want to position themselves as leaders in innovation and sustainability, as it encourages more efficient use of natural resources, minimizes the negative impact on the environment and reduces dependence on virgin raw materials.
ENVIRONMENTAL BENEFITS OF EFFICIENT AND SUSTAINABLE WEEE MANAGEMENT

Recycling and proper management of WEEE offers a number of environmental benefits that go beyond simply reducing waste:
Reducing pollution
WEEE contains hazardous substances that, if not managed properly, can leach into soil and water, contaminating entire ecosystems. Lead, mercury and cadmium are some of the materials that can cause serious health problems if released into the environment.
Saving energy and reducing the carbon footprint
Recycling WEEE saves a significant amount of energy compared to extracting and processing new materials. For example, recycling aluminium from electronic devices consumes 95% less energy than producing new aluminium. In this way, recycling WEEE contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, helping to mitigate climate change.
Conserving natural resources
Many of the materials present in WEEE, such as rare metals, are limited resources. By recycling these components, we can reduce the need to extract new raw materials from the earth, preserving natural resources for future generations.
CHALLENGES TO REDUCING THE ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACT OF WEEE

The main challenges in managing Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) are as follows:
-
- Lack of awareness and education:
Many people are unaware of the environmental impact of WEEE if it is not recycled properly. For example, did you know that an old television can release toxic substances if it ends up in a landfill? However, many people continue to throw these devices into the regular trash. - Insufficient infrastructure and collection systems:
Although there are clean points to deposit WEEE, they are not always easy for everyone to access. A clear example is when you have an old mobile phone at home that you no longer use, but you cannot find a nearby place to leave it for recycling. The lack of an accessible and efficient collection system complicates the process for users. - Regulatory complexity:
The laws on WEEE management vary in each country and, in many cases, are complicated to follow. In addition, small businesses sometimes do not have the resources to understand and apply all the regulations. To do this, it is necessary to seek advice from leading companies with extensive experience in comprehensive waste management, as they are a guarantee of compliance with current regulations. - Lack of eco-design:
Many electronic products are not designed to facilitate recycling. For example, some devices have batteries or components that cannot be easily separated, making it difficult to recover valuable materials. If products were designed from the beginning with recycling in mind, the efficiency of the process could be improved. - Rapid technological evolution:
Technology advances rapidly, making devices obsolete in just a few years. This generates an increasing volume of WEEE. A clear example is the life cycle of mobile phones: many people replace them every two or three years, creating a large number of devices that must be recycled. - Recovery of valuable materials:
Many electronic devices contain precious metals such as gold and silver, but extracting them efficiently requires advanced technologies. In many cases, the lack of adequate infrastructure means that these materials are not recovered, wasting valuable resources. Recycling a million mobile phones, for example, could recover several kg of gold. - Joining the Circular Economy:
One of the great solutions is to encourage the repair and reuse of electronic devices, but this is not always easy or accessible. Instead of throwing away a laptop that has a fault, what if we could repair it affordably? Implementing a true circular economy in the WEEE sector remains a challenge, but there are companies that are making it an increasingly common practice. - Adapting to new types of waste:
With the emergence of new types of electronic devices, new waste also arises. WEEE is not just phones or televisions, it now includes drones, electric cars and smart devices such as voice assistants. Managing this new waste requires recycling systems to continually adapt.
- Lack of awareness and education:
BEST PRACTICES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC WASTE (WEEE)
Did you know that an old mobile phone contains valuable metals such as gold and silver that can be recovered? What do you do if your tablet, microwave or smartwatch breaks down?
Here are some practical recommendations so that we can all contribute to efficient management of our WEEE. Take note and think about how many of these actions you currently carry out and which ones you can start putting into practice:
-
- Extend the useful life of devices: try to repair rather than replace. Often, a small repair can significantly extend the useful life of an electronic device.
- Responsible recycling: dispose of devices at specialized collection points.
- Reuse: before throwing away a device, consider donating it to organizations that can give it a second life.
- Smart shopping: choose products from brands that offer recycling options and are committed to sustainability.
- Education and awareness: awareness is key.
TMA CARRIES OUT INTEGRAL, EFFICIENT AND SUSTAINABLE MANAGEMENT OF WEEE
At TMA (Tecnología Medio Ambiente) we are committed to the comprehensive management of WEEE, helping companies implement efficient recycling systems and contributing to the Circular Economy.
Electronic waste requires special treatment, not only in recycling, but also in its collection, storage and transport.
We are committed to being part of the solution, promoting the comprehensive and efficient management of waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE). We offer comprehensive solutions ranging from collection and transport to specialized treatment and recovery of electronic waste.
We have advanced technology to maximize the recovery of valuable materials and minimize the environmental impact, guaranteeing a complete management cycle.
At TMA we analyze and implement the most appropriate recycling and recovery solutions for each type of waste, ensuring its reintegration into the production cycle while taking care of both our clients and the environment.
Our fleet of vehicles, equipped with the latest loading and transport systems, guarantees an agile and effective logistics service, allowing us to transport any type of waste to our treatment facilities. By having our own fleet dedicated to transporting all types of waste, we ensure the traceability of the process from start to finish.
We have a specialized technical team that is responsible for identifying and classifying the different types of materials, offering sustainable solutions that optimize both time and costs for our clients.
THE CIRCULAR ECONOMY IN WEEE MANAGEMENT
Technology is present and also future. We must see the usefulness and functionality it has at the present time without leaving aside its potential future contribution, both when using it and when disposing of it.
With the rise of technology, the production of this waste has increased exponentially. This implies designing products that can be repaired, reused and recycled.
According to the United Nations, 53.6 million tons of electronic waste were generated worldwide in 2023 alone, but only 17.4% was recycled properly.
At TMA we work with the Zero Waste philosophy, transforming waste into new resources and thus contributing to the Circular Economy while minimizing its environmental impact.
The correct management of WEEE is a commitment that we must assume jointly, both at a personal and business level. By adopting practices that encourage the reduction, reuse and recycling of this waste, we avoid harming the environment and help conserve natural resources and promote the Circular Economy.
At TMA, we continue to work to offer comprehensive solutions that guarantee efficient and sustainable management of WEEE, making technology and sustainability the path to a future that is more respectful of our planet.
We take care of our clients and we take care of the environment.
We are much more than comprehensive waste management.
Do you need efficient waste management or more information about the services we offer at TMA? Write to us at comercial@tma.es and we will be happy to provide you with a personalized proposal, fully adapted to your needs.
Discover our comprehensive Waste Management Services.
Follow us on TMA’s LinkedIn. Subscribe to our YouTube channel.
Contact us, we will be happy to advise and inform you.




